The insurance industry has the opportunity to drive sustainability through circular claims management. By keeping resources in the circle, avoiding waste and shifting from a "replace-first" to a "repair-first" mindset, insurers can significantly reduce carbon emissions - particularly in the claims function, which accounts for the vast majority of operational emissions. This approach not only aligns with new EU regulations and the transition to a low-carbon economy, but also offers compelling business benefits, including cost reduction, operational efficiency, and enhanced customer engagement. This document explores how leading insurers are embracing circularity, the regulatory landscape driving these changes, and the role of technology and partnerships in building a more sustainable and resilient future.
Feeding the Circle - Saving Emissions and Costs
Circularity in claims management offers insurers a powerful, multifaceted lever for sustainability and business growth. It is a critical path to dramatically reducing carbon emissions, especially since the claims function accounts for 85% of operational insurance emissions, according to McKinsey.1 The shift to circularity directly supports the transition to a low-carbon economy and ensures compliance with increasingly stringent reporting requirements for supply chain emissions (Scope 3).
Beyond environmental benefits, adopting circularity is a sound business decision, delivering tangible reductions in costs and boosting operational efficiency. Furthermore, it is a powerful tool for customer engagement. Claims become a real-world opportunity to build and retain strong customer relationships by supporting their own sustainability ambitions.
Embracing these practices bolsters an insurer's reputation, demonstrating genuine "green credentials," and ultimately helps to "build back better" by supporting resilient rebuilding efforts and long-term insurability.2
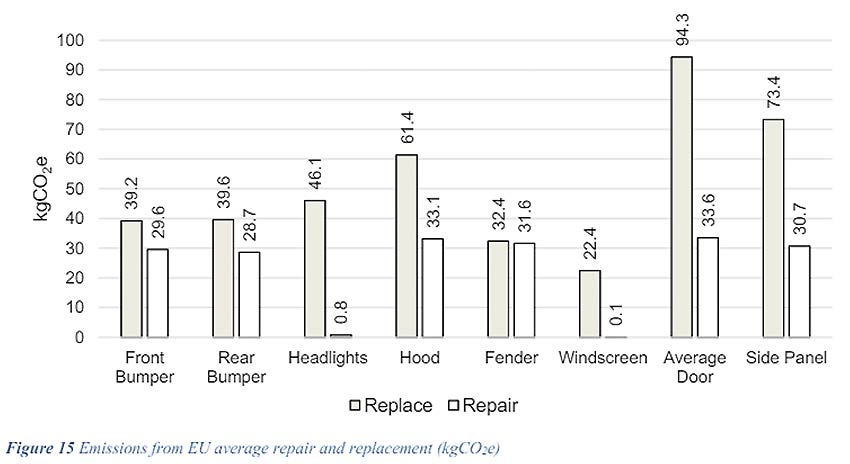
Repair over Replace
Circularity requires keeping resources aka vehicle parts or building materials for insurance claims in the economic circle as long as possible. Repairing is a key concept in order to achieve a circular approach.
Various studies show that repairing a vehicle part results in significantly lower greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than replacing it. Allianz Center for Technology (AZT) for example, compared the repair and replacement processes for nine different parts across four different European countries. The results are clear and similar in all regions - carbon emissions of repair options are significantly lower than replacing with new parts and even with used parts.3
Furthermore, to support the freedom of repair choice, the EU issued the Repair Clause in 2024. This clause grants vehicle manufacturers complete protection for the design of their new cars, but guarantees that this protection does not cover visible spare parts (like car body panels, headlamps, and windscreens). Consequently, these parts can be manufactured, distributed, and utilised freely for repair work in the aftermarket.
Main Drivers for Sustainable Claims Settlement
There are a number of factors driving a shift towards a circular approach to claims management, and the two below are particularly pertinent.
EU Regulation
A new EU regulation in 2024 was a push for circularity and a wake-up call for companies to move the needle in this direction - the European Union introduced the Circular Economy Action Plan. The plan addresses the fact that 50% of all GHG emissions and over 90% of biodiversity loss and water stress result from the extraction and processing of resources. This plan is a coordinated initiative under the European Green Deal, aiming for a climate-neutral, resource-efficient, and competitive economy. Expanding the circular economy is expected to be crucial in reaching climate neutrality by 2050 and separating economic growth from resource consumption, all while securing the EU's enduring competitive edge.

Mounting Pressure for Claims Cost Management
A recent study by the German Insurance Association (GDV) revealed that claims costs are rising above the inflation rate; for example, car back doors are now twice as expensive as 10 years ago.4 Managing costs is a key motivation for implementing sustainable claims procedures. When insurers focus on repairs instead of replacements, utilise resilient and energy-saving materials, and minimise waste, they can decrease payout amounts while providing lasting benefit to their customers.
Furthermore, these eco-conscious methods contribute to a reduction in both how often and how severe future claims are, as climate-proof repairs, for example, lead to lower overall expenditures. Employing digital solutions and environmentally sound workflows also boosts operational effectiveness, thereby lowering overhead costs.
Partners are Key
Claims settlement in general relies on proven partners - and this is even more true for sustainable claims. Insurers need not only repair partners but also partners who provide sustainability-related data and analytics. Development of markets for used parts takes time - but early players, like ClaimParts in Germany, play a significant role in building out the market.
For motor claims data and analytics, Eco Repair Score®, a Belgian-founded, Europe-wide Software as a Service (SaaS) solution, helps insurers, fleets, and repair networks enhance sustainability in claims management. The platform uses seamless API integration to conduct automated Life Cycle Assessments (LCA), which precisely quantify CO2 emissions and other environmental impacts. A significant finding shows a positive correlation between sustainability and cost reduction: A 1% improvement in the relative Eco Repair Score corresponds to a €17.99 decrease in the cost per repair.
France Leads the Way in Sustainable Motor Claims
France is leading Europe in sustainable vehicle end-of-life (ELV) management, utilising structured infrastructure and advanced dismantling processes.The country has surpassed EU goals with impressive rates: an 86.9% reuse and recycling rate and a 94.2% reuse and recovery rate. This success is heavily supported by the organisation Recycler Mon Véhicule (RMV), which fosters collaboration between automakers, recyclers, and dismantlers. Automakers like Renault and Stellantis are actively supporting RMV's circular economy efforts.5, 6
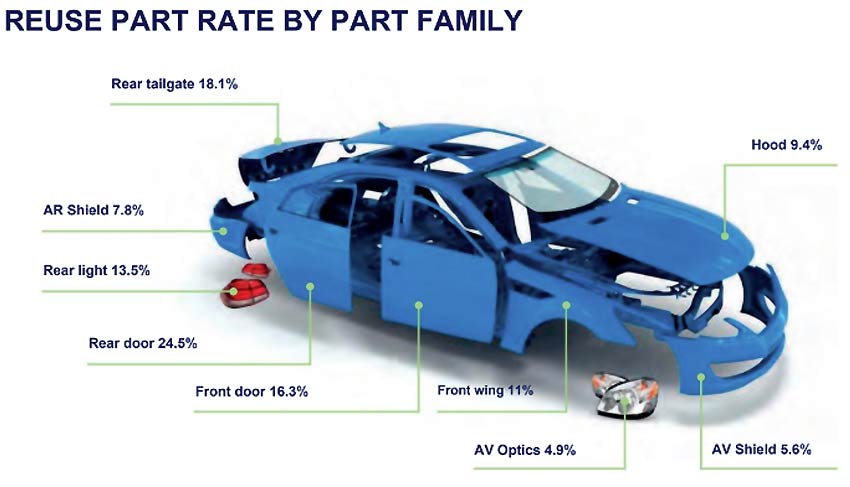
AXA has introduced Alpha Scale, a program designed to implement circular repair methods throughout Europe. This initiative has already yielded concrete outcomes: 21% of repair claims now incorporate at least one salvaged component, leading to an average savings of €256 per claim. The immediate plan for Alpha Scale is to enhance its offerings by expanding the inventory of reused parts and striving for a 10 percentage point rise in their adoption rate. Looking ahead, the mid-term goal is to double the usage of alternative parts, capitalising on the new Alpha Scale distribution framework and supportive regulatory shifts.7
Covéa, a leading motor insurer, is focused on promoting sustainable repairs, as 2023 data showed only 29% of damaged parts were fixed and a mere 4.9% of replacement parts were salvaged. The insurer's strategy involves engaging all stakeholders, including repair specialists, recyclers, policyholders, and manufacturers, who are informed by vehicle repairability data from Covéa’s technology centre, CESVI France. Stéphane Duroule, Chief Insurance Officer France stated: “Insurance companies are working hard day after day with their partners to improve their performance and tackle the carbon impact of the repairs they cover for their customers. This means they play a key role in advancing sustainable repairs.”8, 9
Germany Started the Journey
Allianz Insurance in Germany has launched an initiative, starting in April 2024, to promote the use of certified used car parts salvaged from total-loss vehicles. The goal is to reuse undamaged components, such as doors and fenders, to support circularity. Over 1,400 Allianz partner workshops are currently offering repairs using these certified used parts, though safety-critical components like steering systems and rims are excluded.10
"Our analysis makes it clear how crucial the choice of the type of repair process is for the CO2 balance. In the event of collision damage, vehicle exterior parts are always affected, for which professional repairs are generally possible. These parts are still too often replaced with new parts. A repair is significantly more resource-efficient," says Dr. Christoph Lauterwasser, Head of the Allianz Center for Technology.11, 12
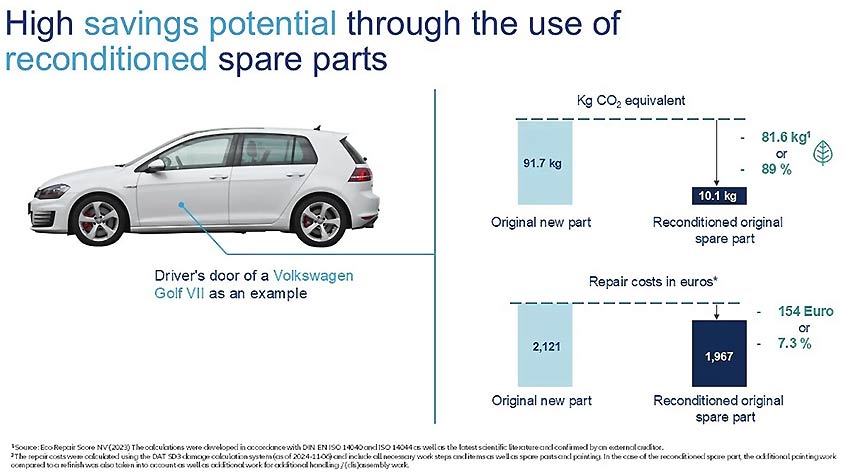
The Allianz Center for Technology (AZT) analyzed the environmental and financial impact of vehicle repairs versus part replacement. Similar to findings mentioned above, their study, conducted with Oakdene Hollins/Metsims, found that the "Repair before Replace" principle is generally more environmentally friendly and cost-effective. For example, repairing a defective LED headlamp or cracked windscreen can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by approximately 99% compared to installing a new part.13
Challenges of Sustainable Claims Management
The path to sustainable claims management often comes with some challenges. Insurers must first overcome higher initial costs, requiring upfront investment in technology, eco-friendly materials, and staff training, which can be prohibitive for smaller companies. Compounding this, a limited availability of qualified suppliers can slow down processing, particularly in rural regions. Also, it will take time before the markets for used vehicle parts are established and delivering on their promise.
In addition, customer resistance remains a hurdle, as some policyholders may be unwilling to embrace sustainable options if they fear they are more expensive or less reliable. The complex integration of new sustainable workflows with existing, often legacy, processes demands extensive overhauling and retraining, inevitably leading to temporary operational disruptions.14
Technology as the Foundation
Sustainability-related data and analytics like carbon emissions increase the complexity in claims due to additional metrics needing to be calculated and monitored. At the same time these new metrics enable innovative insights and parameters for claims steering and management.
Cloud-based core platforms like Guidewire provide the agility and flexibility that is needed to incorporate carbon emissions and nature-related data points, as well as various insurtech solutions around sustainability, directly into the core insurance processes. Curated applications and content via Marketplace enable insurers to innovate more quickly, and leverage data and analytics via their core platforms - so claims teams have it at their fingertips when they need it.
1 Source : https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/financial-services/our-insights/decarbonizing-p-and-c-claims
2 Source photo : https://www.azt-automotive.com/_Resources/Persistent/2f45e03259a22b3a5390863e1ed956fd3f1b9732/AZT-Report_Repair%20or%20Replace_Final%20Version.pdf
3 Source : https://www.azt-automotive.com/_Resources/Persistent/2f45e03259a22b3a5390863e1ed956fd3f1b9732/AZT-Report_Repair%20or%20Replace_Final%20Version.pdf
4 Source : https://www.gdv.de/gdv/medien/medieninformationen/ersatzteilpreise-steigen-um-sechs-prozent-reparaturkosten-belasten-kfz-versicherer-193328
5 Source : https://autorecyclingworld.com/transformation-of-auto-recycling-in-france-europes-first-auto-eco-organization-leads-the-way/
6 Source photo : https://www.covea.com/sites/default/files/2024-05/Livre_blanc_Covea_la_reparation_durable_en_automobile.pdf
7 Source : https://www-axa-com.cdn.axa-contento-118412.eu/www-axa-com/43c9962e-0132-4d99-b72e-23a798e7a494_AXA_Unlock_Sustainable_Insurance.pdf
8 Source : https://www.covea.com/en/analysis/sustainable-vehicle-repairs-environmental-social-and-societal-issue
9 Source : image translated from Covea white paper ‘Sustainable Automotive Repair’ p 52
10 Source : https://www.allianz.com/de/mediencenter/news/artikel/250721-reparaturen-neu-denken-gut-fuers-geschaeft-die-kunden-und-den-planeten.html
11 Source : https://www.azt-automotive.com/en/topics/RepairOrReplaceEn
12 Source : https://www.allianz.com/de/mediencenter/news/artikel/250721-reparaturen-neu-denken-gut-fuers-geschaeft-die-kunden-und-den-planeten.html
13 Source : https://www.azt-automotive.com/en/topics/RepairOrReplaceEn
14 Source : https://www.aranca.com/knowledge-library/articles/business-research/sustainability-in-action-transforming-p-c-claims-management